Frontend Quickstart, build your first dApp
This tutorial will guide you through the process of building a frontend that interacts with smart contracts on ZKsync. The frontend will allow users to pay fees with any ERC20 tokens using a paymaster.
What you'll learn:
- How to build frontend
- How to send transactions through a paymaster
Tools:
- - zksync-cli
- - zksync-ethers
- - Hardhat
In this tutorial we're going to:
- Create a basic frontend to interact with a smart contract deployed in ZKsync.
- Learn about
zksync-ethersand use it to connect to ZKsync and interact with our contract. - Learn about paymasters.
- Integrate a paymaster in our frontend to allow users to pay transaction fees in any ERC20 token.
Prerequisites
- Download and install Node.js.
- Use the
yarnornpmpackage manager. We recommend usingyarn. To installyarn, follow the Yarn installation guide. - Get some ERC20 tokens. The easiest way is to mint TEST tokens directly in our explorer. You can also get Sepolia USDC or DAI from the Aave faucet and then bridge them to ZKsync using the ZKsync bridge.
Setting Up the Project
We're going use the Vue.js web framework to build this app although
the process is similar with other frameworks like React.
In addition, we're going to use the zksync-ethers SDK, which extends ethers with ZKsync-specific features.
First, create a new project folder called frontend-paymaster.
mkdir frontend-paymaster
cd frontend-paymaster
Deploying the Greeter Contract
Next, let's deploy a simple Greeter contract that we can
use for testing.
Make a new contracts folder using the zksync-cli command below:
npx zksync-cli create contracts --template hardhat_solidity
Enter the private key you will use for deployment when prompted.
Then, move into the contracts folder and compile the template contracts.
npm run compile
Finally, deploy the Greeter contract by running the template deploy script.
Make sure to save the deployed contract address for the next section.
npm run deploy
Setting Up the Frontend
Move out of the contracts folder and back into main project folder, and create a new frontend project with Vue.
npm create vue@latest --project-name frontend -- --typescript
Then, move into the frontend folder and install the project dependencies below.
npm install ethers zksync-ethers
Next, replace the code in src/App.vue with the template code below:
Project Structure
We'll only work in the <script> section of the ./src/App.vue file.
Some methods are already provided while other have to be implemented.
We'll go through these ones one by one:
// METHODS TO BE IMPLEMENTED
const initializeProviderAndSigner = async () => {
// TODO: initialize provider and signer based on `window.ethereum`
};
const getGreeting = async () => {
// TODO: return the current greeting
return '';
};
const getFee = async () => {
// TODO: return formatted fee
return '';
};
const getBalance = async () => {
// TODO: Return formatted balance
return '';
};
const getOverrides = async () => {
const from = await signer?.getAddress();
let overrides: TransactionLike = { from };
if (selectedToken?.value?.l2Address != L2_BASE_TOKEN_ADDRESS) {
// TODO: Return data for the paymaster
}
return overrides;
};
Add the Contract Info
Update the .env file in the frontend folder to add the VITE_GREETER_CONTRACT_ADDRESS variable
with the deployed contract address from the previous section.
VITE_GREETER_CONTRACT_ADDRESS=<0x_YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS>
Initialise Provider and Signer
The initializeProviderAndSigner function in ./src/App.vue is called right after the connection to Metamask is successful.
In this function we should:
- Initialize a
BrowserProviderand aSignerto interact with ZKsync. - Initialize the
Contractobject to interact with theGreetercontract we deployed previously.
- Import the necessary classes from
zksync-ethersin the import statement we added previously:src/App.vueimport { Contract, BrowserProvider, Provider, utils, type types, Signer, type Wallet } from 'zksync-ethers'; - Initialise the provider, signer, and contract instances like this:src/App.vue
const initializeProviderAndSigner = async () => { provider = new Provider('https://sepolia.era.zksync.dev'); // Note that we still need to get the Metamask signer const browserProvider = new BrowserProvider(thisWindow.ethereum); signer = Signer.from(await browserProvider.getSigner(), networkChainId, provider); contract = new Contract(GREETER_CONTRACT_ADDRESS, GREETER_CONTRACT_ABI.abi, signer); };
zksync-ethers extends the existing classes from ethers with zksync-specific methods so,
unless you're using any of those features, you won't need to do any changes in your code.
Note that classes like Contract and Provider have the same constructor parameters.Retrieve the Greeting
Fill in the function to retrieve the greeting from the smart contract:
const getGreeting = async () => {
// Smart contract calls work the same way as in `ethers`
const greeting = await contract?.greet();
return greeting;
};
Now, after connecting the Metamask wallet to ZKsync Sepolia Testnet, you will see the following page:
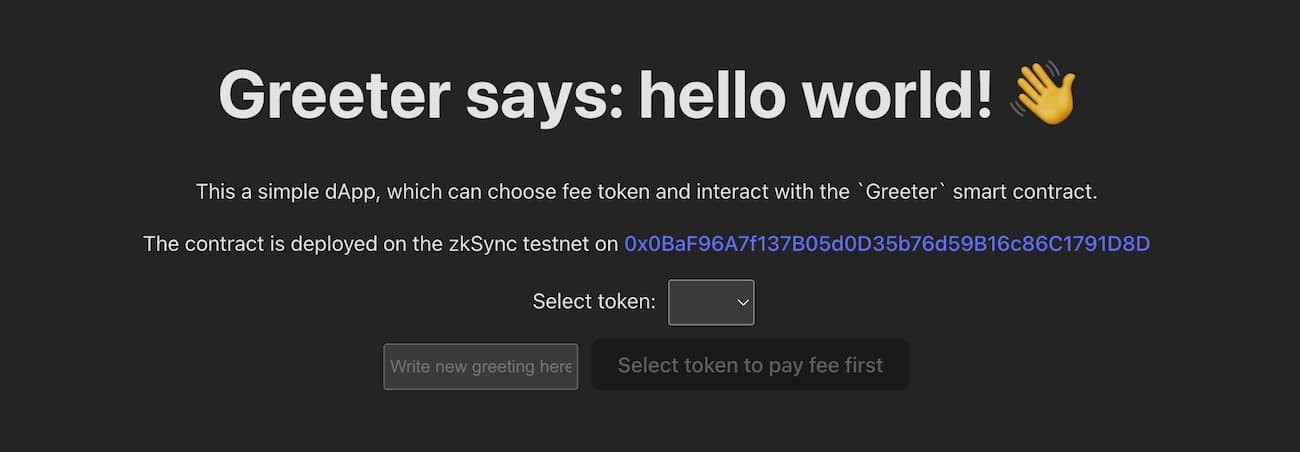
The "select token" dropdown menu allows you to choose which token to pay fees with. We'll enable this feature later.
Check Balance and Estimate Fee
The easiest way to retrieve the user's balance is to use the Signer.getBalance function.
- Add the following dependencies to the same place you added imports before:
import { formatUnits } from 'ethers'; - Implement the
getFee()method that will estimate how much will it cost to update the message in theGreeter.solcontract calling thesetGreetingmethod:const getFee = async () => { // Getting the amount of gas (gas) needed for one transaction const feeInGas = await contract?.setGreeting.estimateGas(newGreeting.value); // Getting the gas price per one erg. For now, it is the same for all tokens. const gasPriceInUnits = await provider?.getGasPrice(); // To display the number of tokens in the human-readable format, we need to format them, // e.g. if feeInGas*gasPriceInUnits returns 500000000000000000 wei of ETH, we want to display 0.5 ETH the user return formatUnits(feeInGas! * gasPriceInUnits!, selectedToken?.value?.decimals); }; - Implement the
getBalance()function as shown below:const getBalance = async () => { // Getting the balance for the signer in the selected token console.log(selectedToken?.value); const balanceInUnits = await signer?.getBalance(selectedToken?.value?.l2Address); // To display the number of tokens in the human-readable format, we need to format them, // e.g. if balanceInUnits returns 500000000000000000 wei of ETH, we want to display 0.5 ETH the user return formatUnits(balanceInUnits!, selectedToken?.value?.decimals); };
Now, when you select the token to pay the fee, both the account balance and the expected fee for the transaction will be displayed.
You can enter the message you want to save and click Refresh to recalculate the fee. Note that the fee depends on the length of the message that we want to store in the contract.
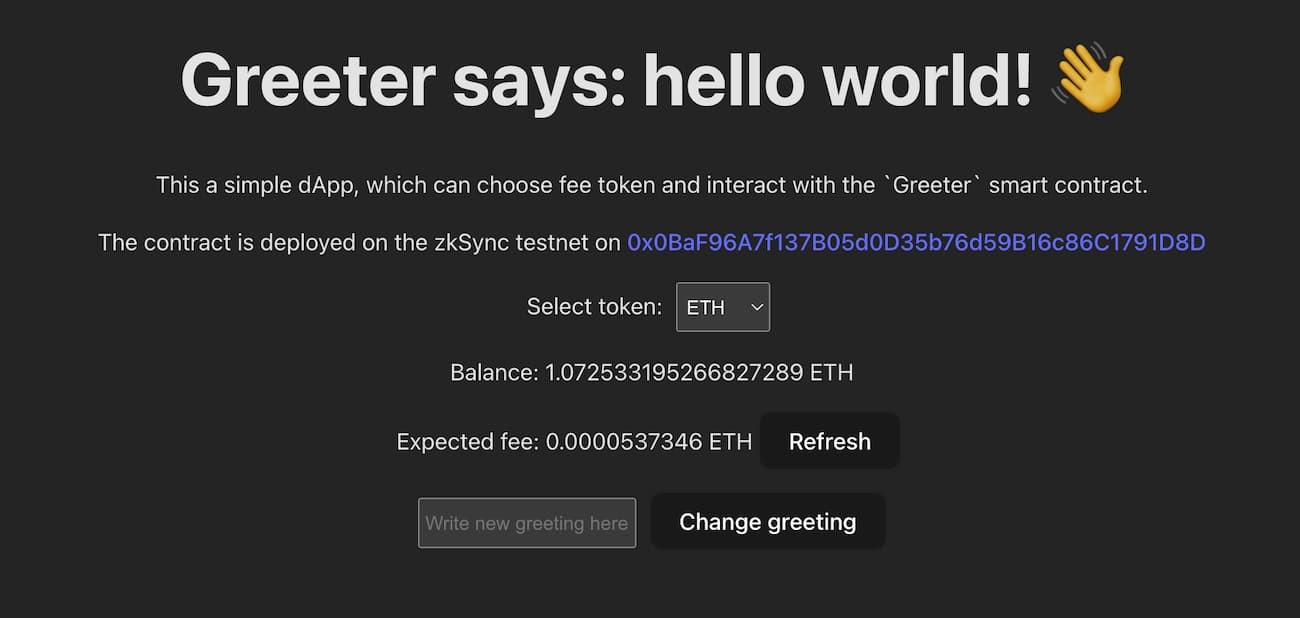
It is possible to also click on the Change greeting button, but nothing will happen yet as we haven't implemented the function. Let's implement that next.
Update the Greeting
Update the changeGreeting function in ./src/App.vue with the following code:
const changeGreeting = async () => {
txStatus.value = 1;
try {
const overrides = await getOverrides();
const txHandle = await contract?.setGreeting(newGreeting.value, overrides);
txStatus.value = 2;
// Wait until the transaction is committed
await txHandle.wait();
txStatus.value = 3;
// Update greeting
greeting.value = await getGreeting();
retrievingFee.value = true;
retrievingBalance.value = true;
// Update balance and fee
currentBalance.value = await getBalance();
currentFee.value = await getFee();
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
alert(e);
}
txStatus.value = 0;
retrievingFee.value = false;
retrievingBalance.value = false;
newGreeting.value = '';
};
Now you can update the greeting message in the contract via a transaction sent with Metamask. Once the transaction is processed, you will see the Greeter message change on the app.
Congrats! You now have a fully functional Greeter-dApp! However, it does not yet leverage any ZKsync-specific features. Let's fix that by integrating a paymaster!
Refresh your browser, or open the Metamask extension on your browser and click Next or Cancel to resolve it.
Read more about
wallet_requestPermissions, in the MetaMask documentation.Pay Fees with ERC20 Tokens
ZKsync Era has native account abstraction, a feature that allows application developers to integrate paymasters. You can find more information about paymasters in this section of our docs but the TL;DR is the following:
- Paymasters are smart contracts that alter the fee mechanism of the protocol.
- The paymaster contract pays the transaction fees with ETH using its own balance.
- Instead of forcing users to just pay transaction fees with ETH, the paymaster contract logic dictates what can be done.
- From a user's point of view, paymasters can allow users to pay gas fess with ERC20 tokens or even allow gasless transactions.
- To integrate a paymaster in your app, transactions must include specific parameters as transaction overrides in a custom property called
paymasterParams.
We will use the testnet paymaster that is provided on all ZKsync Era testnets.
This means that transaction fees in tokens with fewer decimals than ETH will be bigger; for example, USDC which has only 6 decimals. This is a known behaviour of the testnet paymaster, which was built for demonstration purposes only.
As the name suggests, the testnet paymaster is only available on testnet. When integrating your protocol on mainnet, you should follow the documentation of the paymaster you use, or create your own.
The getOverrides function returns an empty object when users decide to pay with Ether but,
when users select the ERC20 option, it should return the paymaster address and all the information required to interact with it.
Let's see how it's done.
- The first step to allow payments with ERC20 tokens is to add them to the dropdown selector. Right now the dropdown selector only shows ETH.
To add more options, uncomment some of the tokens within the
allowedTokensvariable or add your own. - To retrieve the address of the testnet paymaster we'll use the
getTestnetPaymasterAddressmethod from the ZKsync provider. This is one of the zksync-specific methods provided byzksync-ethers:const getOverrides = async () => { const from = await signer?.getAddress(); let overrides: TransactionLike = { from }; if (selectedToken?.value?.l2Address != L2_BASE_TOKEN_ADDRESS) { // TODO: Return data for the paymaster } return overrides; };
- We need to calculate how many tokens are required to process the transaction.
Since the testnet paymaster exchanges any ERC20 token to ETH at a 1:1 rate, the amount is the same as the ETH amount in wei:
const getOverrides = async () => { const from = await signer?.getAddress(); let overrides: types.TransactionLike = { from }; if (selectedToken?.value?.l2Address != utils.L2_BASE_TOKEN_ADDRESS) { let testnetPaymaster = import.meta.env.VITE_TESTNET_PAYMASTER_ADDRESS; if (!testnetPaymaster) { testnetPaymaster = await provider!.getTestnetPaymasterAddress(); } const gasPrice = await provider!.getGasPrice(); // define paymaster parameters for gas estimation const paramsForFeeEstimation = utils.getPaymasterParams(testnetPaymaster!, { type: 'ApprovalBased', minimalAllowance: BigInt('1'), token: selectedToken.value!.l2Address, innerInput: new Uint8Array(), }); // estimate gasLimit via paymaster const gasLimit = await contract!.setGreeting.estimateGas(newGreeting.value, { customData: { gasPerPubdata: utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT, paymasterParams: paramsForFeeEstimation, }, }); // fee calculated in ETH will be the same in // ERC20 token using the testnet paymaster const fee = gasPrice * gasLimit; - Now, what is left is to encode the
paymasterInputfollowing the protocol requirements and return the needed overrides.
This will be the complete function:const getOverrides = async () => { const from = await signer?.getAddress(); let overrides: types.TransactionLike = { from }; if (selectedToken?.value?.l2Address != utils.L2_BASE_TOKEN_ADDRESS) { let testnetPaymaster = import.meta.env.VITE_TESTNET_PAYMASTER_ADDRESS; if (!testnetPaymaster) { testnetPaymaster = await provider!.getTestnetPaymasterAddress(); } const gasPrice = await provider!.getGasPrice(); // define paymaster parameters for gas estimation const paramsForFeeEstimation = utils.getPaymasterParams(testnetPaymaster!, { type: 'ApprovalBased', minimalAllowance: BigInt('1'), token: selectedToken.value!.l2Address, innerInput: new Uint8Array(), }); // estimate gasLimit via paymaster const gasLimit = await contract!.setGreeting.estimateGas(newGreeting.value, { customData: { gasPerPubdata: utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT, paymasterParams: paramsForFeeEstimation, }, }); // fee calculated in ETH will be the same in // ERC20 token using the testnet paymaster const fee = gasPrice * gasLimit; const paymasterParams = utils.getPaymasterParams(testnetPaymaster!, { type: 'ApprovalBased', token: selectedToken.value!.l2Address, // provide estimated fee as allowance minimalAllowance: fee, // empty bytes as testnet paymaster does not use innerInput innerInput: new Uint8Array(), }); overrides = { ...overrides, maxFeePerGas: gasPrice, maxPriorityFeePerGas: BigInt(1), gasLimit, customData: { gasPerPubdata: utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT, paymasterParams, }, }; } return overrides; };
TheApprovalBasedtype in thepaymasterParamsindicates that this paymaster allows ERC20 tokens. Behind the scenes, ZKsync Era will take care of approving the ERC20 spending.
Complete Application
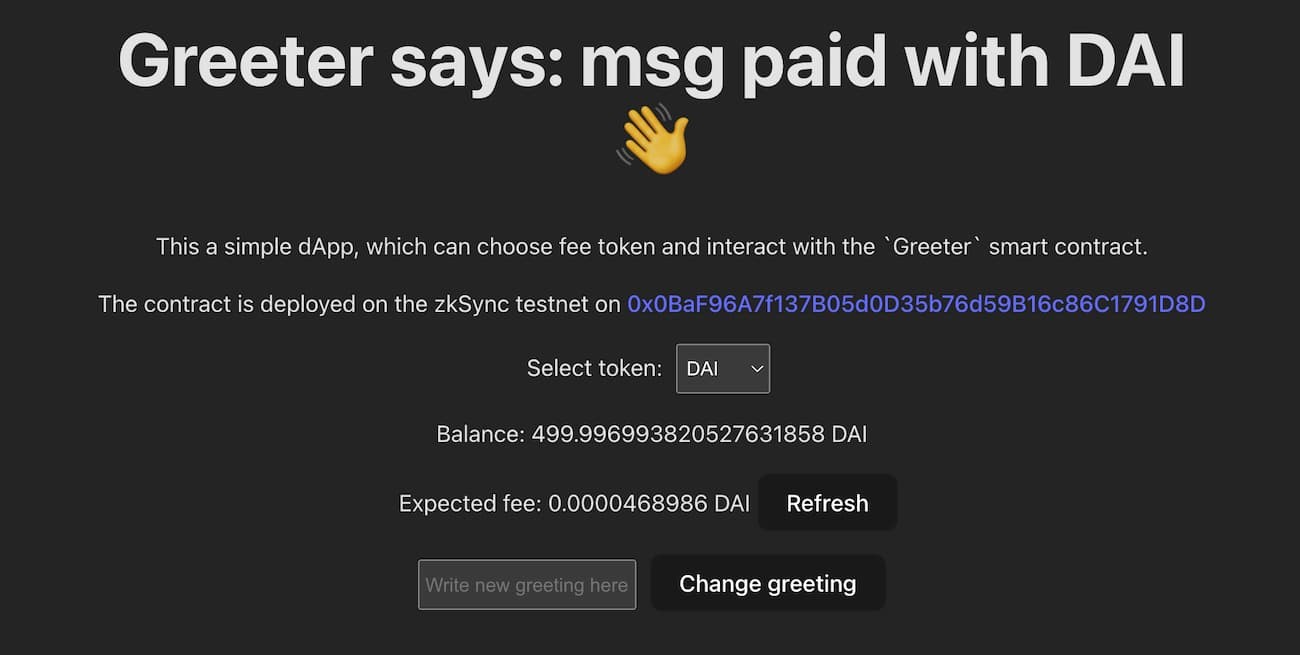
Now you should be able to update the greeting message with ETH or any of the available tokens.
- To test out the application, start the development server, and navigate to
http://localhost:5173/in your browser.npm run dev - Select one of the ERC20 tokens to see the estimated fee:
- Click on the
Change greetingbutton to update the message. Since thepaymasterParamswere supplied, the transaction will be anEIP712(more on EIP712 here) so it will look slightly different in your wallet:
- Click "Sign" to send the transaction.
After the transaction is processed, the page updates the balances and the new greeting can be viewed.
You've paid for this transaction with an ERC20 token using the testnet paymaster 🎉
Takeaways
zksync-ethersis a Javascript library that extendsetherswith ZKsync-specific methods.- Paymasters allow users to pay transaction fees in ERC20 tokens or gasless.
- Paymasters can be easily integrated in frontend applications by including additional transaction parameters.
Next steps
- For an overview of security and best practices for developing on ZKsync Era, refer to the Security and best practices page.
- To learn more about the
zksync-ethersSDK, check out its documentation. - To learn more about the ZKsync hardhat plugins, check out their documentation.
- If you have a project, check out our migration guide.